GitLab Developer FAQ: Difference between revisions
m →Create repository clone: adjusting file name |
|||
| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
'''Note:''' insert <span style="color:yellow; background:red; bold"> ''your token number''</span> | '''Note:''' insert <span style="color:yellow; background:red; bold"> ''your token number''</span> | ||
== Working with forks == | |||
=== I have a clone of the main repository and want to connect it now to my fork === | |||
'''Note:''' <span style="color:yellow; background:red">'''User.Space'''</span> needs to be replaced by your user space, see the link in the web interface. | |||
replace <span style="color:white; background:green">'''pct-online'''</span> by repository you are working with. | |||
Check the remotes of your repository | |||
git remote -v | |||
Should show you something like | |||
origin git@git.app.uib.no:pct/pct-online.git (fetch) | |||
origin git@git.app.uib.no:pct/pct-online.git (push) | |||
Since ''origin'' should refer to your development proxy, we first rename the current ''origin'' to ''upstream'': | |||
git remote rename origin upstream | |||
Add the fork as the new ''origin'': | |||
git remote add origin git@git.app.uib.no:<span style="color:red">User.Space</span>/<span style="color:green">pct-online</span>.git | |||
Synchronize with the fork | |||
git remote update | |||
Make your branches to track the branches of your fork, e.g. for the ''dev'' branch: | |||
git checkout dev | |||
git branch --set-upstream-to origin/dev | |||
Check the remotes: | |||
git remote -v | |||
With new result: | |||
origin git@git.app.uib.no:User.Space/pct-online.git (fetch) | |||
origin git@git.app.uib.no:User.Space/pct-online.git (push) | |||
upstream git@git.app.uib.no:pct/pct-online.git (fetch) | |||
upstream git@git.app.uib.no:pct/pct-online.git (push) | |||
Revision as of 21:30, 9 February 2021
Main Page -> Documentation -> Gitlab Developer FAQ
This is a collection of frequently asked Gitlab questions for developers
Please edit this page and add your question, or send email to pCT@uib.no
Authentication
In order to clone non-public repositories and do synchronization, an authentication method is required. It is recommended to use SSH keys
Register SSH key
- Login to https://git.app.uib.no
- go to User settings -> SSH Keys (https://git.app.uib.no/-/profile/keys)
- paste public SSH key from your
.sshfolder, something likeid_*.pub - select optionally a title and expiration date
- click Add
Create access token
- Login to https://git.app.uib.no
- go to User settings -> Access Tokens (https://git.app.uib.no/-/profile/personal_access_tokens)
- Choose name and expiration date and scopes
- click Create personal access token
- Store the token in a safe place or configure the relevant application for accessing the repository with this token immediately
Hints:
- Create access tokens only for the scope with the minimal access permissions required for your purpose
- Keep in mind: the token is only visible in the web interface after creation, you can not get it later
- Unused tokens should be revoked as soon as possible
Create repository clone
A repository clone is your work copy, it is created using the git clone-command.
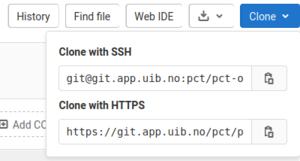
Find the links for the repository to be cloned
Clone using SSH
An SSH key needs to be configured -> Gitlab Developer FAQ#Register SSH key
git clone git@git.app.uib.no:pct/pct-online.git
Note: this is an example for the pct-online repository
Clone using Access Token
An access token needs to be configured -> Gitlab Developer FAQ#Create access token
git clone https://gitlab-ci-token:your-token-number@git.app.uib.no/pct/pct-online
Note: insert your token number
Working with forks
I have a clone of the main repository and want to connect it now to my fork
Note: User.Space needs to be replaced by your user space, see the link in the web interface. replace pct-online by repository you are working with.
Check the remotes of your repository
git remote -v
Should show you something like
origin git@git.app.uib.no:pct/pct-online.git (fetch) origin git@git.app.uib.no:pct/pct-online.git (push)
Since origin should refer to your development proxy, we first rename the current origin to upstream:
git remote rename origin upstream
Add the fork as the new origin:
git remote add origin git@git.app.uib.no:User.Space/pct-online.git
Synchronize with the fork
git remote update
Make your branches to track the branches of your fork, e.g. for the dev branch:
git checkout dev git branch --set-upstream-to origin/dev
Check the remotes:
git remote -v
With new result:
origin git@git.app.uib.no:User.Space/pct-online.git (fetch) origin git@git.app.uib.no:User.Space/pct-online.git (push) upstream git@git.app.uib.no:pct/pct-online.git (fetch) upstream git@git.app.uib.no:pct/pct-online.git (push)