Using IPbus: Difference between revisions
Created page with "Main Page -> Control & Readout Software Documentation and Howto's -> Using IPbus" |
|||
| (19 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Main Page]] -> [[Control & Readout Software Documentation and Howto's]] -> [[Using IPbus]] | [[Main Page]] -> [[Control & Readout Software Documentation and Howto's]] -> [[Using IPbus]] | ||
== Use case == | |||
IPbus is a control protocol that uses UDP/IP to send values into the registers on the readout unit (RU). The software on the host computer uses the Hardware Access Library (uHAL) to send the commands to the RU. | |||
[[File:ipbus-conect6.png|750px]] | |||
== Configuration files == | |||
There is a main connection file (pRU-connections.xml), this file contains the address and port of the RU, for information on the content of the connection file please see the [[:Media:PRU Ethernet Configurations.pdf | pRU Ethernet Configurations]] document. | |||
Following there is a Module registers file (module-address.xml), this file contains a table with all the registers present in the RU. | |||
Finally, there are files for each register | |||
* global_regs.xml | |||
* trigger_manager.xml | |||
* offload.xml | |||
* alpide_control.xml | |||
* alpide_data.xml | |||
As of the writing of this page, these files can be found on the production_test repository in the ipbus branch under the BSP folder. | |||
WARNING: To prevent undefined behavior the register files MUST match the firmware version! | |||
== Smart Dummy Hardware == | |||
To be able to read values from registers, a custom DummyHardwareUdp.exe can be built from this repository: | |||
[https://github.com/norscope/ipbus-software/tree/smartdummy IPbus Custom Repo] | |||
NOTE: Remember to switch to the smartdummy branch. | |||
This adds a file reader in the DummyHardware.cpp that reads a file in the directory of the executable, the file is called register-values.txt, an example file can be found here: [[:Media:register-values.txt | Example file]] | |||
=== How to Build on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS === | |||
==== Requierd packages ==== | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | |||
$ sudo apt update | |||
$ sudo apt install git g++ make erlang python3 python-is-python3 libboost1.71-all-dev libpugixml-dev | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
==== Building ==== | |||
In the directory where the repository have been downloaded: | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | |||
$ make | |||
$ sudo make install prefix=/home/user/ipbus-install | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
==== Adding paths to envirorment ==== | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | |||
$ export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/home/user/ipbus-install/lib:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH | |||
$ export PYTHONPATH=/home/user/ipbus-install/lib/python3.8/site-packages:$PYTHONPATH | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
==== Running the hardware emulator ==== | |||
Change directory to ipbus-install/bin/uhal/tests | |||
NOTE: Make sure the register-values.txt file is present in this folder. Filename is in all lowercase. | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | |||
./DummyHardwareUdp.exe -p 50001 -v 2 -V | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
==== Testing the emulator ==== | |||
From the production_test repo, in the folder tests_vcu118 run: | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | |||
$ python test_ipbus_emulator.py | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
This should output 0xfeedbeef | |||
== Additonal information == | |||
For more information, please consult the IPbus wiki at: [https://ipbus.web.cern.ch/ipbus/doc/user/html/software/uhalQuickTutorial.html IPbus wiki] | |||
Latest revision as of 14:22, 24 September 2021
Main Page -> Control & Readout Software Documentation and Howto's -> Using IPbus
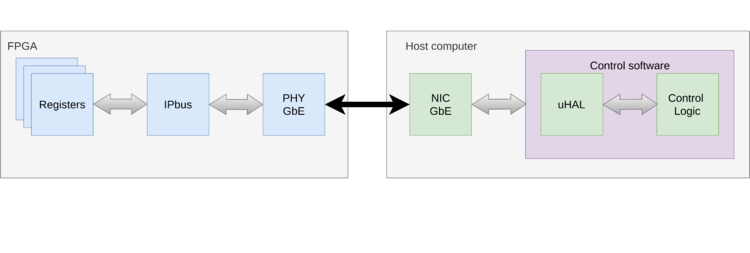
Use case
IPbus is a control protocol that uses UDP/IP to send values into the registers on the readout unit (RU). The software on the host computer uses the Hardware Access Library (uHAL) to send the commands to the RU.
Configuration files
There is a main connection file (pRU-connections.xml), this file contains the address and port of the RU, for information on the content of the connection file please see the pRU Ethernet Configurations document.
Following there is a Module registers file (module-address.xml), this file contains a table with all the registers present in the RU.
Finally, there are files for each register
- global_regs.xml
- trigger_manager.xml
- offload.xml
- alpide_control.xml
- alpide_data.xml
As of the writing of this page, these files can be found on the production_test repository in the ipbus branch under the BSP folder.
WARNING: To prevent undefined behavior the register files MUST match the firmware version!
Smart Dummy Hardware
To be able to read values from registers, a custom DummyHardwareUdp.exe can be built from this repository: IPbus Custom Repo NOTE: Remember to switch to the smartdummy branch.
This adds a file reader in the DummyHardware.cpp that reads a file in the directory of the executable, the file is called register-values.txt, an example file can be found here: Example file
How to Build on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS
Requierd packages
$ sudo apt update
$ sudo apt install git g++ make erlang python3 python-is-python3 libboost1.71-all-dev libpugixml-devBuilding
In the directory where the repository have been downloaded:
$ make
$ sudo make install prefix=/home/user/ipbus-installAdding paths to envirorment
$ export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/home/user/ipbus-install/lib:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH
$ export PYTHONPATH=/home/user/ipbus-install/lib/python3.8/site-packages:$PYTHONPATHRunning the hardware emulator
Change directory to ipbus-install/bin/uhal/tests NOTE: Make sure the register-values.txt file is present in this folder. Filename is in all lowercase.
./DummyHardwareUdp.exe -p 50001 -v 2 -VTesting the emulator
From the production_test repo, in the folder tests_vcu118 run:
$ python test_ipbus_emulator.pyThis should output 0xfeedbeef
Additonal information
For more information, please consult the IPbus wiki at: IPbus wiki
